Week 1 - Overview on Change
- need to thrive in an environment of rapid and continuous change
Change and it is purpose
- change is the process of becoming different
- forces us to evolve
- keeps live interesting and challenges us
- creates a massive opportunity to have a clearer vision, become stronger, reinvent, grow and thrive
Change intensity levels
-
Minor - do not require change in behavior or process
- get an office chair
-
Moderate - within one group and requires some change in behavior
- e.g. introducing a new sports routine
-
Significant
- highly complex, cross functional, needs a change in several behaviors and/or have a steep learning curve - e.g. an organizational change
- significant time investment
-
Extreme
- e.g. covide
- novel in nature, poorly understood
- sudden and broad
- fear and speed
- highly uncertain
Change and drivers
- driven by availability of information and speed with which we can share that information
Difference between transformation and change
-
change has clear boundaries
- is forced among us
- simple
-
transformation has no clear boundaries
- cuts across different departments
- involves complex changes that includes individuals and different speed of adoption
- higher risk and uncertainty
- more difficult to manage
- needs experimentation
- takes longer than change
- is done by attention from us
- requires commitment
- is intentional
- requires action and active participation
- consists of a portfolio of initiatives or actions
- deep and radical
Agile Transformation
- why: to thrive in an environment with high change saturation
- flexible mindset and welcome and embrace change
- process of becoming mentally and emotionally resistent when dealing with change
Change Management Theories
- Theories - diffusion of innovation and theory of transition
- explain how we respond to change and how we behave
Diffusion of innovation
- E.M Rogers - Diffusion of Innovation
- Innovators 3%
- Early adopters 14%
- Early majority 34%
- Late majority 34%
- Laggards 16%
By Rogers Everett - Based on Rogers, E. (1962) Diffusion of innovations. Free Press, London, NY, USA., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=18525407
Theory of transition
Transition - any event that changes an individuals assumption, roles, relations
Valley of dispair - the emotional impact change has on us
Could be used the access a groups current emotional status when running through a change
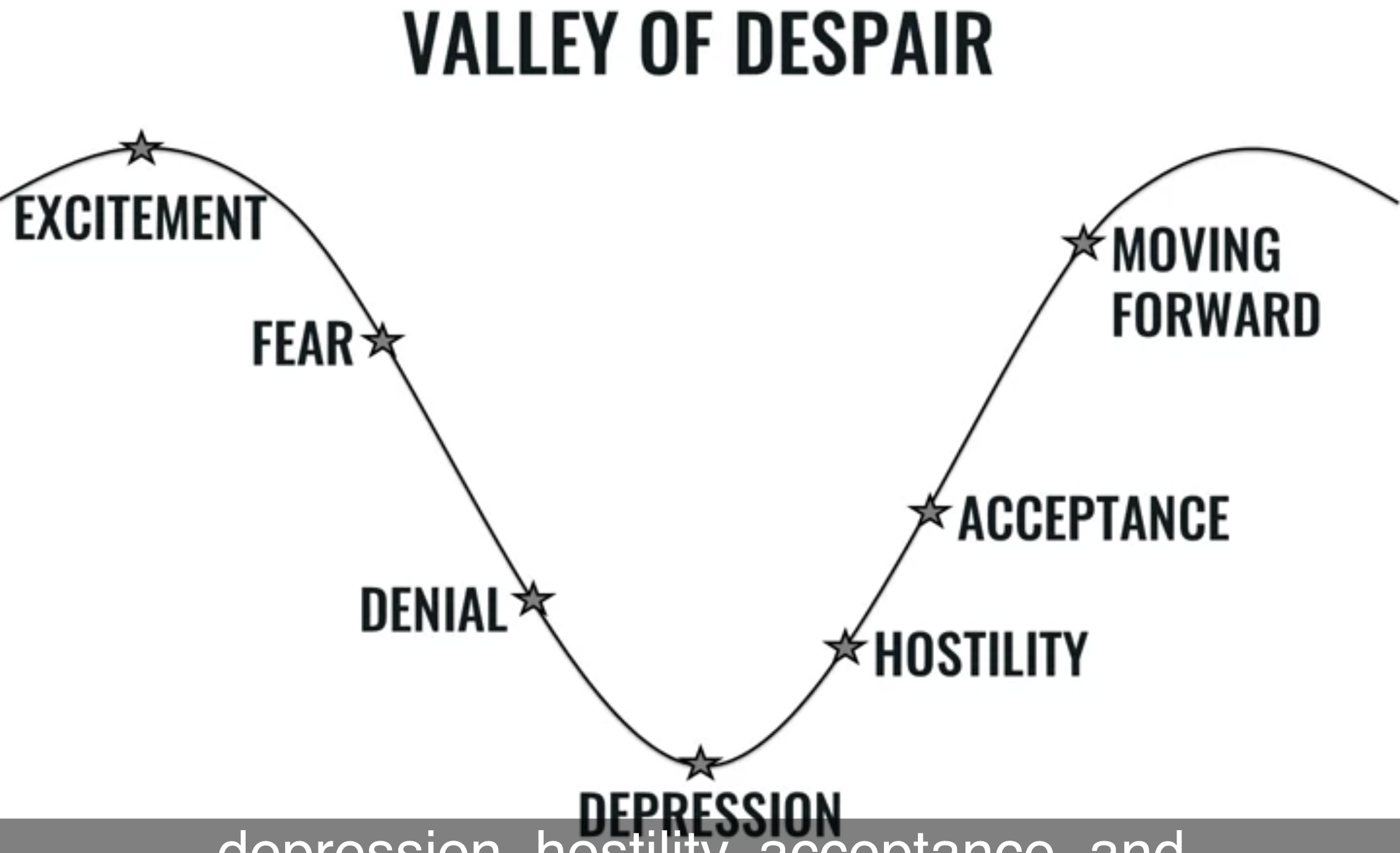
- has an emotional impact on us
Week 2 - Agile Leadership
traditional leader
- fixed mindset, manages ins a linear, rigid way within a command and control framework
- relying on top-down approach
- little room for creativity and innovation
- risk averse
- uncomfortable with change
- see themselves as an expert
- close to other’s input
- relies on individuals
- direct others
- predictable
Agile Leader
- with a growth mindset, empowers teams and organizations to observe, experiment and innovate within a servant leader framework
- seek out development
- high believe that organizational change is a positive thing
- flexibility
- mentor and analyze
- servant leadership relies on inquiry
- ability to tolerate risk
- comfortable with change
- adaptable in problem solving approach
- mentoring
- values teams vs. individuals
- listening and asking questions
Attributes Mindset and Behaviors
- traditional is not sufficient to thrive in current fast changing environments
Agile Personal Assessment
[[AgilePersonalAssessment.pdf]]
- I feel anxious, worried or overwhelmed in my life. 0
- I feel like my environment is stressful. 0
- I’m fearful of what the future holds. 0
- I reflect on my fears or worries. 2
- I feel comfortable with change. 2
- I go out of my way to seek change. 2
- I prioritize my personal needs over others’ demands. 1
- I feel confident in my skills and abilities to adapt to the future. 2
- I enjoy changing priorities and projects. 1
- Reflect on the last 12 months of your life. On a scale of 1 (Not at All!) to 10 (I Can Handle Anything!), how comfortable are you with changes in life and work? 2
Week 3 - Agile and Teams
Traditional team
- A traditional team is a team of individuals assigned to a project to deliver a specific prescribed outcome appropriate to the individual’s level of expertise.
- rigid, well documented process
- change averse
- prio policies and procedures over team or customer
- unmotivated
- siloes
- function on learned helplessness
- interact on a minimal basis
- work at an unregulated pace
Mission as a agile leaders to harness motivation and creativity of the individuals on your team.
Agile Team
- The Agile team is a self-organizing team of motivated individuals who are focused on delivering the most value to its customers in the shortest time possible.
- Agile Manifesto reference

Agile Leader for an Agile Team
- team as a reflection of your leadership
Team agility baseline assessment
[[TeamAgilityAssessment.pdf]]
- Team embraces change easily 1
- Team continuously reflects on its performance and takes action to improve 1
- Team members are comfortable bringing up difficult topics and challenges 1
- Team works at a sustainable pace 1
- Team has a well-defined process for resolving conflicts 1
- Team members subscribe to at least three of the following values: Courage, Respect, Commitment, Openness, and Focus 1
- Team welcomes last-minute changes 1
- Members of the team work through constant changes together 1
- Members of the team understand their roles and responsibilities 1
- Team members feel supported and empowered to do their best work 1
Week 4 - Agile and Organizations
Traditional organization
- stable an rigid structures, rules, policies, procedures
- top down management and siloed departments
- unhappy and slowing down results
- stables and fixed
- top down hierarchy
- siloes
- bureaucracy
- individuals seen as a commodity
Agile Organization
- These are organizations that are variable, dynamic, they have flexible structure, and they’re nimble in their response to change
- answer to
- accelerated pace of change
- advances in tech
- competition for the best talent

[[AgileOrganisationAssessment.pdf]]
- Organization is open to new ideas and innovation 1
- Employees in the organization know why changes happen 1
- Leadership has high change quotient (CQ) 1
- Leadership across the organization supports, mentors and empowers employees to do their best work 1
- Organization supports employees through change 1
- New projects and initiatives get approval fast 1
- Organization is prepared to respond to environmental changes quickly 1
- Change management team participates in large complex initiatives 1
- Employees are officially recognized as the greatest organizational resource 1
- Agile and Continuous improvement principles and philosophy are practiced throughout the organization 1
Certificate
Linking
Notes mentioning this note
Change management
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0 Transitional//EN” “http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40/loose.dtd”>
Change Management